intestinal amebiasis (amebnaya dysentery) - is infection by pathogenic strains of protozoa Entamoeba histolytica (intestinal amoeba), striking a person of the large intestine.
What is amebiasis, how to treat it, how to avoid it, and what mechanisms, properly, takes this unpleasant disease - will be discussed in today's publication.
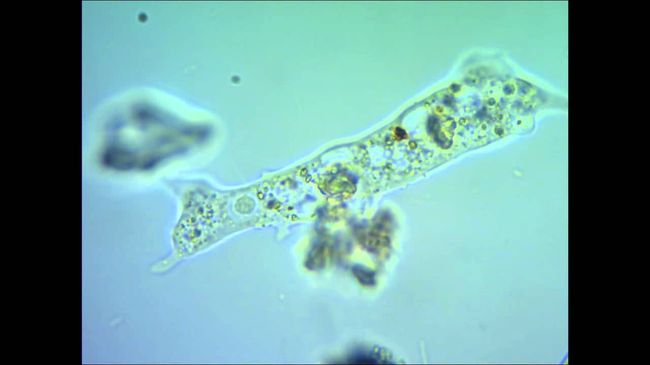
Amoebiasis - disease, has spread primarily in the tropical and subtropical climatic zones in countries with low levels of sanitation. but, it can occur almost everywhere.
Statistics
In underdeveloped countries, according to the statistical studies of mortality from parasitic intestinal diseases, amoebiasis - the most common cause of death. order 480 millions of people around the world are permanent carriers of intestinal amoeba, in 48 million subsequently arise colitis and develop extra-intestinal amoebiasis, and for 40-100 thousands of patients illness, Alas, have been fatal. Due to uncontrolled mass migration, deterioration in the economies of many countries and the lack of proper sanitary controls accelerates the spread of disease amebiasis in the world, and, of course, increased number of cases of this disease.

disease progression
amoeba life cycle consists of the following stages:
autonomic (trofozoitnaya) stage, four embodiments for which the amoeba may be formed in such -
- tissue form (It is present in affected tissues during acute process),
- forma magna,
- form minutes,
- predtsistnaya;
cyst stage, which, properly, It ensures the safety of the organisms in the outer (outside the body) environment. They were detected in feces from tsistonositeley accident or preventive inspection, as well as in convalescent under dispensary observation.
epidemiology data
Infection is transmitted by the fecal-oral mechanism, and its source is human. Usually the cyst amoebae are allocated to the external environment with faeces. The feces contained in a daily amount, the thousands, and sometimes millions of units. Vegetative options Entamoeba histolytica remain viable outside of the intestine of all 15 – 30 minutes, but her cysts when outside the body are resistant and can survive depending on the conditions of 3 days (at medium temperatures) to 111 days at low temperature air. On the surface of the skin, they live only a few minutes, under the fingernails can survive for about an hour, and in the body of the fly - order 2 days. Getting in dairy products, Cysts remain alive about 15 days at room temperature. Survival of microorganisms, generally, It is highly dependent on the component temperature, structure and ambient humidity.
So, amebiasis can be transmitted through contact with:
- soil,
- wastewater,
- household items,
- water from open reservoirs,
- vegetables, fruit, other food,
- contaminated hands.

note! Intestinal amebiasis carriers often does not manifest itself in any way, its symptoms are absent, that does not prevent these clinically healthy people in large numbers to allocate cysts into the environment and become a source of infection.
Infected amebiasis may equally as an adult, and child, In women, this disease occurs with the same frequency, as men. Amoebiasis in adults as well, as well as in children, caused, usually, failure to comply with hygiene rules, when the child does not wash their hands before eating after a walk or an adult eating unwashed fruits and vegetables. Most often ill amebiasis persons over five years.
Pathogenesis
cysts, swallowed by man, ekstsistatsiyu pass in the small intestine by the action of enzymes. Thereafter released outwardly from the fission process in the simplest appear 8 individuals such as single-core (trophozoites), which move in the upper sections of the colon, where they begin their parasitism. Going further, trophozoites take the form of four- odnoâdernyh or cysts, excreted in the faeces.
- Asymptomatic carriage is typical for the situation, When amoebae are found in the large intestine and feed on detritus, bacterial organisms and fungi.
- Under certain conditions - a massive invasion, violations of the physico-chemical properties of the intestinal environment, as well as its peristalsis, for inflammation and micro-traumas mucous, dysbacteriosis and helminths, immunodeficiency, hormonal failures, under stress and starvation - just a transition into a state forma magna, fabric becoming parasites. Attaching to the intestinal wall mucous, they begin to secrete tissue-dissolving enzymes, some of whom are hyaluronidase, which facilitates the further penetration of the parasite into the fabric.
- Contacting neutrophils, amoeba lyse them, thus facilitating separation monooksidantov, which further accelerate the melting process of tissue. As a result, the intestinal wall collapses, at the mucosal surface pores appear, its protective properties are reduced by several times. The deposition of the areas of ulceration, It happens poisoning organism products amoebae disintegration, growth of pathogenic intestinal microflora, and further deepen the simplest in intestinal tissue continues.
- The parasite multiplies in the wall of the intestine and leads to microabscesses, autopsied inside the intestine with subsequent formation of ulcerative hearth diameter from 2 mm 1 cm. The edges of the pockets of the rough, its bottom is lined with brownish necrosis products. If not for amebiasis is a difficult character, the mucous membrane between the centers usually looks, and the affected area may look different - small erosion and large ulcerative lesions, reaching a size of a few centimeters, coexist with areas of healing.
- As a result of flowing in parallel healing ulcerative lesions are replaced by granulation tissue, which leads to a fibrotic changes and stenosis of the lumen of the large intestine.
- The chronic form is characterized amoebiasis pseudopolyps (ameʙom) against the backdrop of massive ulceration of the mucous. Polyps are distributed to the skin of the perianal and perineal areas, causing the treatment of patients in the first place to the gynecologist.
- ulcers, reaching serous membrane intestine, become a cause of formation perikolitov, but with the defeat of the main vessels develop profuse bleeding from the gut.
- When a massive common amoebic parasite infestation occurs resettlement in the liver, lung tissue, occasionally - in the brain and other organs. In this case, the affected structures are formed amebic abscess. From the right liver sections abscessed formation are revealed in the bile ducts, in the abdomen and under the pleura.

Diagnostics
Amoebiasis develops under the control of the immune system, generating specific antibodies. Immunity is not lifelong, reinfection and re-invasion at amebiasis are taking place.
Diagnosis amebiasis set according anamnestic epidemiology, on the basis of visible manifestations of disease and using laboratory methods for diagnosis.
- Parasitological diagnosis of amebiasis is placed in the identification of the sample taken for analysis of tissue or forma magna parasite, and - trophozoites-erythrophage. As a model for the study taking swabs from the rectum, mud, Biopsy samples from sites of ulceration, aspirate of abscess. If only the luminal form of the parasite and the cysts were found in a smear - it can not be the sole basis for diagnosis, "amebiasis". Cal analysis is taken repeatedly and fresh, immediately after defecation.
- If there is a severe clinical disease, and in the material parasites could not be detected - used serological methods - ELISA, DGC etc.. d. These techniques make it possible to diagnose amebiasis in 75% patients, suffering from intestinal form of the disease.
- Also suitable technique amoebic antigen detection in feces and PCR reaction.

intestinal amebiasis and its symptoms
WHO amoebiasis is divided into two types of flow.
Manifestnaya
- intestinal form
- extraenteric
asymptomatic
Symptomatic amoebiasis, in turn, is divided into acute and chronic colitis, Besides, severity - on heavy, moderate and mild forms of the disease.
Acute intestinal form
- The incubation period can last from one week to several months.
- At the initial stage, patients complain of acceleration to 6 time / day of bowel movements, stool while unformed and comprise component slimy.
- Then, the amount increases to defecation 20 in a day, and stool take the form of "raspberry jelly".
In this case, the patient may otherwise feel satisfactory, temperature curve changes only slightly or remains normal.
- Temperature rise, vomiting, nausea, loss of appetite and sharp abdominal pain with tenesmus talk about the development of severe disease.
On palpation - belly soft, marked tenderness along the colon. Endoscopically detected characteristic ulcers, appearance which has already been described above.
- Acute stage lasts about 4-6 weeks, after which there is a remission lasting from a few weeks to a few months.
- Then the disease resumes, becomes chronic, lasting for years in the absence of an adequate therapy.The chronic form occurs with recurrent or continuous.
- When the flow of recurrent disease in the form of periods of dyspeptic disorders and pain in the ileocecal region followed by periods of visible health. In periods of exacerbations the patient feels well, Body temperature changes, periodically there are disorders stool. Occasionally there are attacks of abdominal pain, mistaken for appendicitis.
- In the continuous embodiment, remission of chronic amebiasis arises.
Symptoms are largely, constipation alternating with diarrhea, hyperthermia occurs, loss of appetite, abdominal pain are pronounced. Then for a while the symptoms subside, but did not disappear until the end.
Without treatment, the patient is gradually depleted, blood and eosinophilia are observed monocytosis. The patient gets the characteristics of appearance - "bird" person, exhaustion, white or gray coating on the tongue, drawn in the stomach. There are violations of the pulse and heart rate, heart tones - muted. Abdomen could be painful to the iliac region.
When sigmoidoscopy - a characteristic picture with the accession of amoeba.
note! Complications developed intestinal amebiasis have already been listed above, but I would like to separately mention gangrene and perforation of the colon, where the mortality rate of patients without the operation is urgent 100%.
Amebiasis in children often begins immediately with a sharp intoxication: Hyperthermia can reach 40 ° C, the phenomenon of excessive sleepiness, nausea, weakness, vomiting - more pronounced, than adults, for which such a variant of the disease is atypical. Chair - liquid consistency, It contains a large amount of mucous component, the number of bowel movements reaches 15 time / day, rapidly increases dehydration.
Important! Due to rapidly developing dehydration treatment of amebiasis in children must necessarily include measures for rehydration, and it better not to delay.
intestinal amebiasis Treatment
All preparations are divided into amebotsidnye 2 type.
- contact, also called luminal.
- System.
Formulations are assigned to the first type of therapy when the carrier asymptomatic infection and after invasive therapy drugs of the second group in the prophylactic.

The second type of drugs used to treat gastrointestinal and extraintestinal amebiasis abscessed.
In severe course of the disease to the risk of perforation of the intestinal wall and are assigned further occurrence of peritonitis antibiotics, affecting the intestinal microflora.
note! patients, taking corticosteroids, amebiasis can lead to serious complications, eg, to the formation of toxic megacolon. Therefore, all the inhabitants of endemic areas is recommended before prescribing corticosteroids to survey about amebiasis. With a positive result of the study, first appointed amebitsidnaya therapy.
Provided that adequate timely treatment prognosis is almost always favorable until full recovery.

prevention
Preventive measures include early identification of carriers of the disease and sanitation, besides - is necessary to achieve breaking mechanism of transmission of the parasite. risk groups must be examined annually for amebiasis in specialized laboratories. Been ill should be seen by a doctor within 12 months after treatment.
The risk for amebiasis taken include:
- those with gastrointestinal diseases;
- residents of areas, not equipped with sewage;
- workers in the food industry and retailers, working in the field of food;
- workers greenhouses, hothouse, sewerage, treatment facilities;
- homosexuals;
- inhabitants of endemic areas or those, returnees from countries endemic for this infection.
In order to achieve rupture mechanism of transmission of the parasite, produce channeling areas, providing residents quality of drinking water and food, disinfection of potentially contaminated objects and surfaces with the use of chemical agents and boiling. Health education also plays an important role in the prevention of this disease.


