Opisthorchiasis called disease, caused by parasites, which affects mainly the bile duct, liver and pancreas. Symptoms are varied opisthorchiasis, because the disease is difficult to diagnose, and it causes a lot of serious complications. It happens, that the disease infected over the years are not aware of the disease and unsuccessfully treated by different doctors. All this suggests that, that opisthorchiasis - a very important issue and needs to know, opisthorchiasis what and how to treat an illness.
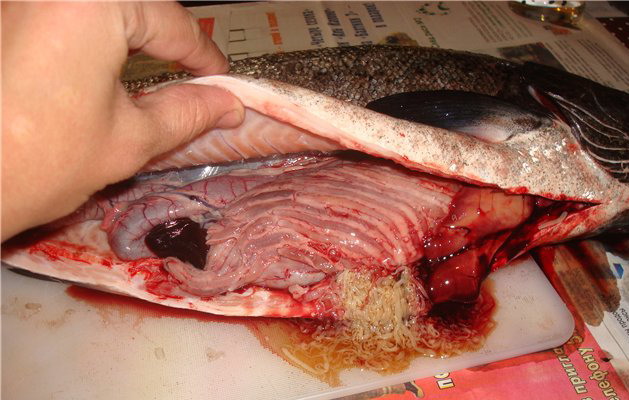
As appears opisthorchiasis
Opisthorchiasis pathogens are Siberian and cat fluke, liver flukes. These parasites are of lanceolate shape and length of the 8 to 17 mm.
Their development takes place by means of two intermediate hosts, and then they get into the human body (or animal), causing disease opisthorchiasis. Activators of parasites in the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts host, postponing eggs there. After, eggs with human feces (or animal) fall into the water bodies, where their inhabitants and swallow water.
Important! Opisthorchiasis human infection occurs through fish, which is a carrier of the parasites. Improperly cooked fish and salted raw fish - the main cause of the disease. In most larvae carriers are fish of the family Cyprinidae: carp, vobla, bream, roach, rudd, ide. Contamination from pike unlikely, from the sturgeon family - impossible.
Once in the human body together with fish eaten, the larvae remain in the intestine, and then penetrate through the walls to the liver and pancreas. after 2 weeks larvae grow into adult worms, which begins to actively lay eggs.
note! The most dangerous region for the dissemination opisthorchiasis - Western Siberia. Frequent cases of the disease occur among residents, inhabiting the banks of the Volga, Kama, Dnipro, Urals.
The adult, its larvae and eggs, getting into the bile duct, applied mechanical and allergic effects on the body:
- mechanical: The worm attaches itself to the mucous membrane of the biliary tract, and it injure their suckers, and causing injury, moving around the gall paths. The injured mucosa can easily penetrate bacterial infections, that contributes to the development of inflammatory processes in the biliary tract.
- allergic: worms secrete waste products, what cause allergic reactions.
Besides, accumulation of parasites in the bile duct provokes bile stasis, than create a favorable environment for the emergence of secondary biliary tract infection.

symptoms opisthorchiasis
Opisthorchiasis symptoms may not manifest themselves for a long time, their appearance depends on the number of larvae, features of the parasite life cycle, frequency of defeat, the individual and the state of the patient's immunity.
There are two types of disease:
- Chronic;
- Acute.
In the case of acute opisthorchiasis from infection to development of the disease can pass from 5 to 40 days (average - 21 day). In this case, the illness lasts no more than a month.
Chronic opisthorchiasis may not manifest themselves for a long time and lasts for decades.
acute opisthorchiasis
The acute stage of the disease is characterized by a bright clinical picture.
The first symptoms:
- The emergence of pain in the right upper quadrant.
- The occurrence of aches in joints and muscles.
- An increase in liver size (typical for women).
- The appearance of vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, frequent heartburn, meteorism (typical for women).
- appetite loss.
Often, the patient manifested erosive gastro, allergic reactions appear, there are disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
Important! On the occurrence of the disease may indicate the appearance of skin rashes. To respond to any changes in the appearance of the skin.
The clinical picture opisthorchiasis in the acute stage is similar to the symptoms of many other infectious diseases. Therefore it is difficult to determine, opisthorchiasis looks like, and it is quite difficult to diagnose.
chronic opisthorchiasis
Symptoms of the disease in the chronic form characteristic of such diseases, like cholecystitis, hepatitis, gastroduodenit, pancreatitis. opisthorchiasis manifestations can be constantly present or occur with a periodicity, alternating periods of exacerbation and remission.
characteristic symptoms:
- Paroxysmal pain in the right upper quadrant.
- Disruption of the functioning of the gallbladder.
- Chest pain.
- Aversion to much fat dishes (typical for women).
- Failure in bowel habits.
- lowering the performance (typical for men).
- The emergence of dizziness and headaches.
- Irritability, sleep disorders.
- The appearance of tremor.
- Depression, depression.
Picture of the disease is often complemented by allergic manifestations: itch, hives, alimentary allergy, angioedema.
Important! Often, disorders of the nervous system, are featured opisthorchiasis, referred to neurology, which contributes to the wrong diagnosis and treatment.
Opisthorchiasis symptoms are not life threatening, but treatment must begin in the early stages of the disease, when it was possible to identify the first signs of illness, otherwise you may develop other diseases of internal organs.
Complications include opisthorchiasis:
- Acute form of pancreatitis;
- Cirrhosis of the liver;
- Stagnation and stop the outflow of bile;
- Abscess;
- Diabetes.
note! In children, the disease can be fixed since the age of one year, and occurs usually in the chronic form. Chronic opisthorchiasis children rarely manifests itself (typically only in the form of allergic reactions) and detected only by means of special methods of diagnosing.

How to identify the disease
In the early period of the disease is difficult to diagnose opisthorchiasis, tk. from the onset of symptoms to the selection of eggs and larvae in the faeces takes place about 5-6 weeks.
Diagnostic measures include:
- anamnesis, where it appears, whether the patient lived in places, where often diagnosed opisthorchiasis, Does the patient happened to take in food poorly thermally processed fish.
- Take the CBC, wherein revealed increased ESR, leukocytosis, high degree of eosinophilia.
- Appointed by the biochemical analysis of blood, showing a decrease of albumin, protein level and the change in liver enzymes.
- Conducted a comprehensive diagnosis (Special markers IgG, IgM, CEC).
- held ultrasound, wherein extension detected bile duct, diffuse changes in the liver, hepatomegaly.
- Appointed by the analysis of feces and duodenal juice for the detection of parasites eggs.
When fecal not immediately possible to detect the pathogen eggs, so laboratory study conducted in triplicate (intervals).
More modern methods of diagnosis are PCR- research (polymerase chain reaction) and immuno-assays.

Regimen opisthorchiasis
Before, how to treat opisthorchiasis, doctor parasitologist appoint an individual treatment plan for each individual case.
To cure opisthorchiasis, use complex treatment:
- Preparatory stage. It can last 10-20 days (depending on the degree of disease severity), and involve administration of drugs to relieve symptoms and improve the overall general condition.
- Degelmentizatsiyu. Prescribers course, aimed at the elimination of helminths. At this stage it is impossible to self-medicate and should strictly adhere to the doctor's recommendations.
- The rehabilitation phase. Aimed at restoring violations, arising in the body due to invasion. Applied choleretic therapy, purgation.
opisthorchiasis treatment of adults in all phases involves mandatory dieting (diet №5, It is prescribed for gastrointestinal infections).
Preparatory stage
In the first stage of treatment task - to remove inflammation, relieve the patient from allergic reactions in the digestive system, adjust the secretion of bile ducts.
used drugs:
- antispasmodics (No-ESP, Dyuspalin, Drotaverinum);
- prokinetiki (Motilak, Motilium);
- Prebiotics and probiotics;
- enzyme preparations (eyebrow pencil, alatrofloxacin).
Amount of time, needed for the preparatory phase, as well as the dosage is determined by the doctor depending on the clinical presentation and severity of the disease.
In acute opistorhoze treatment begins with the removal of intoxication. apply:
- antihistamines;
- Administered a glucose solution (5%-ny), brines;
- antibiotics (accession secondary infection);
- Bile products.
Upon accession, cholestasis added products with ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursofalk, Geptral).
Degelmentizatsiya
When anthelmintic treatment prescribed intake of the following drugs:
- calcium chloride;
- antihistamine (diphenhydramine, suprastin);
- antiparasitic agents (Prazikvintal, Hloksil, bithionol);
- Sedativnыh drugs (valerian, Bromine).
To prevent the development of vasculitis use anti-inflammatory drugs (Butadion, Askorutin).
The most effective drugs in the fight against opisthorchiasis are biltricid, albendazole, Hloksil.
The treatment regimen is established by the doctor individually, tk. a number of drugs have contraindications (pregnancy, serdcheno chronic disease, liver damage, et al.).
Antiglistnaya therapy is complemented by carrying out biliary tract drainage procedures, duodenal intubation.
Infection accession antibiotics additionally appointed.
The rehabilitation phase
During the recovery period applies therapeutic action of anti-inflammatory and tonic values.
Important! At the stage of rehabilitation the patient should regularly defecate. If you own it can not do, laxative use.
used drugs:
- Bile means (Xofitol, allohol);
- antispasmodics;
- Hepatoprotection (Darsil, Geparsil);
- anticholestatic drugs.
At this stage the possible accession of traditional medicine, using herbal decoctions choleretic action.
Important! In acute forms opisthorchiasis cure illness in the home can not be - required hospitalization of the patient in hospital.
After completion of all three stages of treatment, after 3 month, the patient should be retested. If necessary therapeutic measures after repeated 6 months.

prevention
Prevention opisthorchiasis includes compliance measures to prevent contact with the causative agent in the body.
Prevention opisthorchiasis:
- Hygiene rules;
- Compliance with processing and cooking fish;
- epidemiological events.
In mild and moderate forms of opisthorchiasis prognosis is usually very favorable, although cases of re-infestation can not be excluded. digestive, hepatobiliary and immune systems require long recovery, but gradually begin to operate in the normal mode.


