Dangerous diseases meningitis - not such a rarity, among children under one year death rate from this disease is in Russia 15%. This is due to the fact, that meningitis in children develops rapidly due to the insufficient development of the immune system and unformed gematoentsefalitnogo barrier.

In case of delayed medical care meningitis just a few hours can cause death or serious consequences for the organism, leading to permanent disability of the child.
Knowledge of the first symptoms of meningitis, Timely access to a doctor and timely initiation of treatment to help prevent dangerous complications of the disease and save the child.
Where does meningitis in children: hazards
Meningitis can occur, as an independent disease, ie. It is not the result of the body's infection (primary meningitis) or develops, as a complication after, as an infectious agent has passed through the blood-brain barrier and cause inflammation (secondary meningitis).

Most often, the disease is contagious nature, ie. the disease can be transmitted in several ways:
- Airborne (infection media);
- Contact-household (through household items);
- Oral-fecal (with water or food);
- Hematogenous or lymphogenous (through the bloodstream or lymph from the affected organs);
- transmissible (through blood-sucking insects);
- Segmentary-vaskulyarnыm ( from infected otolaryngology, inflamed eye sockets, furknkulov on the neck and face, et al.);
- Cherezplatsentarnym ( during birth from mother to child);
- perineural ( of nervous tissue).
Non-infectious meningitis can cause a variety of open head injuries or back - tumor, traumatic brain and spinal injuries, lupus, etc..
note! Children often become infected with meningitis from other sick people, from animals or through household items.
What can cause meningitis:
- Virus - except, measles, rubella, flu, Coxsackie virus, cytomegalovirus, etc.;
- Bacteria - meningococcus, salmonenellez, staphylococcus, Pseudomonas or Haemophilus influenzae;
- Protozoa - amoeba, Toxoplasma;
- Gribok - Candida, kryptokokky, coccidioidomycosis.
When the viral nature of the disease occurs serous meningitis in children, for bacterial infection - purulent meningitis. In this and in another case there is swelling the shells and brain tissues, worsening of blood microcirculation, It begins to stand out unduly cerebrospinal fluid. As a result of increased intracranial pressure and develops "dropsy" brain (gidrocefaliâ). The toxins penetrate the brain, germs and other harmful microorganisms, that cause brain disorders.
Important! Children under 5 years 60-70% cases causes meningococcal bacteria, carrier which can be, As a person, and animal. Preschoolers and school-age children are more common viral meningitis in the background penetration enteroviruses.
The most frightening kind of meningitis is fulminant meningococcemia. A large amount of meningococcus in the blood permeates, which begins to actively produce toxins. As a result of lightning occur irreversible processes in the body: impaired blood clotting, there are hemorrhages in the skin, It occurs occlusion of small vessels, sepsis occurs. A child dies practically within a few hours from the renal or cardiac failure.
note! For meningitis is characterized by seasonality - outbreaks are more common in winter and spring. Epidemics of meningitis occur every 10-15 years old.
For, appeared to meningitis, insufficiently, to an infectious agent just got into the body - reproduction and activity of pathogens depends on the state of the body's defenses. That is why meningitis are the most susceptible young children (from one year to five years) - their protective barriers are imperfect and unable to resist infectious agents.
The risk group includes children with CNS pathologies, premature babies, newborns, had undergone hypoxia, birth trauma, purulent diseases, intrauterine infection.
Symptoms and warning signs of
Signs of meningitis in children does not depend on the type of pathogen and often similar clinical picture to other infectious diseases.
The clinical picture consists of three main symptoms (meningeal triad), are developing rapidly.
The first signs of meningitis:
- Headache. The pain is intense, a strong character, It arises from the first moments of the disease, usually unexpectedly, It does not have a specific localization. The emergence of pain associated with stimulation of nerve endings and brain edema. Due to the irritability of nerve endings there is pain in places, where nerves extend outwardly. This can be determined with pressure on the respective points: the area around the nose wings, the middle of the forehead, eyeballs, upper lip, alveary.
- vomiting: plentiful ("Fountain"), without nausea, no relief, not associated with food intake.
- High temperature (can reach 40 degrees). Increases in the first hours of the disease and all the while kept in the high figures. The advent of high temperature associated with the intoxication syndrome. This syndrome also includes lethargy, lack of appetite, weakness, blurred consciousness, drowsiness, muscular weakness.
If there are one or two symptoms of meningeal triad, it does not mean, that the child appeared meningitis. Additionally, when disease symptoms are manifested obshchemozgovye:
- Reduced sensitivity threshold (increased light-, zvukochuvsvtitelnost);
- Intracranial hypertension. In infants, it appears large bulging fontanelle. Toddlers older sound when tapped will appear on the skull, like knocking on ripe watermelon.
- convulsions (jumps, vzdragivaniya, tremor) and loss of consciousness - in severe forms of the disease.
Infants become sluggish, sleepy, kapriznichayut, refuse to eat, changing nature of the crying and screaming (high tone emitted sound), cold extremities, face pale (It may be covered by irregular spots).
Older children may experience hallucinations, rave, psychomotor agitation. They try to lie, normally - covered with a blanket with a head, any touch them irritated and cry.
note! Meningococcal meningitis is an important diagnostic criterion - the appearance of hemorrhagic-necrotic rash.
The rash of meningitis in children appears in 90% cases later 6 hours of onset, and is associated with vascular thrombosis, arisen with infection. The rash may be of different sizes and irregular shape, touch - dense. Typical localization - the lower limbs, trunk, buttocks, sclera and the eyelids.
The main symptoms of meningitis in children - the so-called shell symptoms. They can be used to accurately determine the presence and progression of the disease.
How does meningitis:
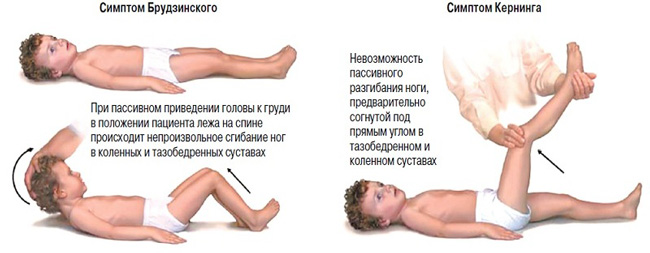
- Stiff neck. You need to put the baby on the back of the head arm and try to bend the head to the chest - in meningitis it will be impossible to make, tk. muscles will be severely shackled. This voltage causes a "meningeal" posture of the child - in the "lying on its side" head thrown back, legs bent to the abdomen.
- symptom Kernig. In the "supine" child carefully bend the leg at the knee and hip joint at a right angle. If the child can not straighten the knee, it is a clear sign of meningitis (for children under 4 months, this feature is not valid).
- symptom Lassazha. Carried out in children under one year. The child is taken into the mouse and it is involuntarily bends the legs to the stomach - impossible to straighten them back.
- symptom Brudzinskogo. To kid, Lying on his back, gently tilt the head to the chest - to automatically bend the arms and legs.
- Symptom "tripod". A child can sit, Only his hands resting on the bed.
Definition of meningeal signs helps parents to recognize the severe pathology and to prevent the development of complications. In children older than 10 years and adolescents should not be ignored such signs, as a severe headache, nausea and stiffness of the cervical spine.
Important! If the child has continuous vomiting, sudden temperature rise to high rates, convulsions, tension neck - need immediate treatment for medical assistance.
The incubation period depends on the meningitis pathogen: for example, meningococcus causes inflammation of the 3-4 day, and Enterovirus meningitis in children - for a week, purulent meningitis in children manifests itself during the first hours of the disease, Viral - characterized by a rapid increase in symptoms followed by fading.
Given the multiplicity of causes of meningitis, requires a thorough examination of a child in a hospital to confirm the exact diagnosis.
Screening for meningitis
Reliably detect the disease only after a series of diagnostic measures, which include:
- Evaluation of meningeal signs (meningeal symptoms).
- General blood analysis. The result is an increase of leukocytes and ESR rates.
- Laboratory examination of the cerebrospinal fluid, lyumbalynaya puncture. When meningitis linkvor milky white, turbid, with a high content of neutrophils, an increased amount of protein.
- bacteriological analysis. Take the fence from the nasopharynx, CSF, blood smears, skin puncture.
- Serology Blood.
The main diagnostic procedure - a lumbar puncture. When this is done a long needle puncture in the lumbar region and takes a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
note! Meningitis examination and inspection of all subjected, who are in contact with the patient, taking into account the severity of the disease course and the rapid spread of the character.
When the survey is important to diagnosis - meningitis or meningismus. When meningism the child will have to attend the same symptoms, but in the cerebrospinal fluid it is not detected changes. This condition is associated with the general intoxication of the organism, without penetrating the infectious agent in the brain. After the appropriate detoxification therapy are manifestations meningism.
How is meningitis in children
Treatment of meningitis in children is carried out only in a hospital. In the case of purulent meningitis applied etiotropic therapy, aimed directly at the destruction of the causative agent. When variant serous meningitis task physicians primarily boils down to reduction of symptoms of infection and keeping the body of the child.
Scheme treatment of meningitis:
- antivirals (interferon, acyclovir, Artepol) - when the viral nature of meningitis.
- Antibacterial broad-spectrum drugs (tsefalosporinы, penicillins) - with bacterial meningitis.
- Providing a specific mode. The child must be in the dark room due to the increased sensitivity to light. It is necessary to create a calm, a healthy psychological environment.
- Infusion therapy - little patient administered with a dropper preparations, enhancing properties of blood, reducing intoxication, as well as with solutions of vitamins for the general maintenance of the organism.
- Normalization intracranial pressure - via diuretics (diuretics): Laziks, furosemide. If the use of diuretics does not give the desired effect, then spend a lumbar (cerebrospinal) puncture.
- Vitamin complexes - to normalize and strengthen the immune system.
- Anticonvulsants and sedatives. (Domosedan, Seduksen).
- light diet: eliminate hot dishes, fatty foods, sweets, marinades, canned goods.
With timely treatment and appropriate treatment of meningitis forecast is favorable: symptoms disappear after 3-4 day, the level of the cerebrospinal fluid returns to normal within 7-10 days. Upon improvement of a patient condition is conducted through 10 days repeated puncture to confirm the fact of recovery.

If later 48 hours after the start of treatment is observed positive dynamics, held repeated lumbar puncture and adjusted medication drugs.
After treatment the child should be seen by a neurologist within two to three months and a year - at the pediatrician, in order to exclude the development of severe consequences. Children after meningitis contraindicated exercise, Stay out of the sun for 5-6 months from the end of therapy.
Consequences and complications
With timely treatment of the effects of meningitis in children are usually kept to a minimum, and after a while they disappear. Complications of meningitis depends on the type of previous infection.
When serous meningitis may be some time after the recovery of the following symptoms occur:
- Poor perception of information;
- Frequent headaches;
- sleep disturbances;
- memory impairment;
- spontaneous seizures.
These effects do not usually wear a pronounced and may periodically occur within five years after suffering meningitis, whereupon usually disappear completely.
When purulent meningitis in a complicated form of the child are usually strongly affects the nervous system. In this connection may be left serious consequences:
- Mental retardation;
- Dysfunction of the motor system;
- Epilepsy;
- Impaired vision and hearing (until their complete loss);
- Paralysis and paresis;
- Violations of the speech apparatus.
AT 5% cases of meningitis in a child under particularly severe forms of the disease complications may occur, leading to death:
- Inflammation of the brain (encephalitis);
- cephaledema;
- Impairment of respiratory and cardiac activity;
- intracranial hypertension;
- Repeated inflammation in the meninges.
When the reactive form of meningitis is likely to survive a child hardly stays- infection for several hours causing toxic shock, drop in blood pressure, disorders of the kidneys and heart, death occurs.
How to prevent meningitis in children
Knowing the cause of meningitis, doctors have developed some measures to prevent the disease.

Prevention of meningitis in children:
- Warning airborne infections: Avoid public places during epidemics of infectious, limiting contact with sick people, protection against infection (wearing cotton-gauze bandages). Many bacteria are killed by ultraviolet light and fresh air, so there will be more than a regular room ventilation and frequent walks in the fresh air.
- Prevention of infections, emerging oral-faecal way - regular personal hygiene: scrubbing, consumed food fruits and vegetables, boiling water etc..
- Vaccination. Immediately vaccinated against meningitis for children - there is no, but vaccinations can help children protect children from a variety of diseases, which may affect the development of meningitis. from pnevmokokka, Haemophilus influenzae, meningococcal vaccinations are not provided, but they can be made on request in the treatment room.
Despite, that meningitis is considered highly dangerous diseases, timely access to physicians with adequate course of therapy a chance to recover completely without complications. The high mortality rate is maintained at chest, impaired children and lightning types of diseases.