Among infectious pathologies meningitis is a leader in mortality. More often than meningitis in adults occur among young people and the elderly, whose immunity is lowered with chronic diseases.

Prevention of meningitis, knowledge of its symptoms and prompt medical care helps to avoid the dire consequences of the disease, among which predominates disability and death.
How could I get meningitis
The cause of meningitis and getting hit in the infectious agent of human brain. The infection destroys the integrity of brain cells, after which it occurs intoxication products harmful microorganisms. The immune system reacts to it the production of prostaglandins, that irritate nerve endings (aching), swelling of tissues and impairment of blood flow.
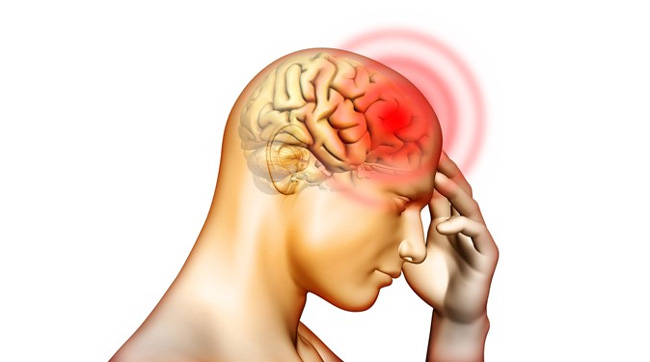
Depending on the causes of infection are two types of meningitis:
- Primary - infection occurs directly meninges, while the inflammatory process does not affect other tissues and organs. For the development of this species often lead meningococcus and viruses.
- Secondary - infection and the development of inflammation is due to ingress of agent in brain membranes from another damaged organ (in abscess, osteomielite, CMT, boils, etc.). The main causative agents here are bacteria - Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococci, colon bacillus, stryeptokokki. One option for the secondary meningitis is an inflammation of tuberculosis, when the TB germs get into the meninges.
Based on this classification, We can identify the main types of pathogens:
- Bacterial meningitis - caused by tuberculosis and E. coli, streptococci and staphylococci, meningococcal and pneumococcal.
- Viral meningitis - infection occurs with viruses: Coxsackie virus, interovirus, influenza virus, herpes, rubella.
- Fungal meningitis - run Cryptococcus, fungus kandydы.
- Protozoan - caused by protozoa: Toxoplasma, amoeba, plazmodyy.
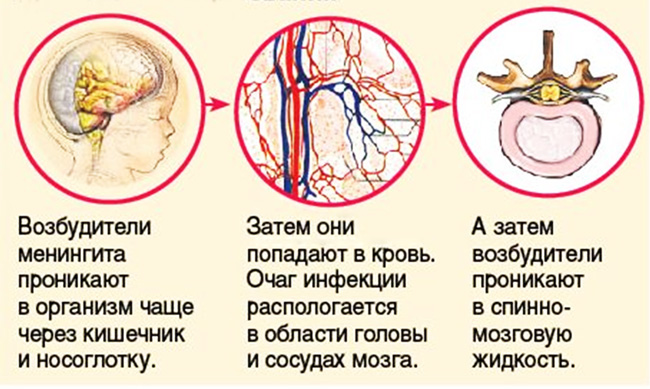
The infectious agent may be absorbed into the body in several ways:
- Airborne (the main and most common way of infection) - You can become infected by a sick person and a carrier of infection by sneezing, coughing, close contact.
- Fecal-oral - infectious agent passes through unwashed hands or food with poor personal hygiene.
- Sexually - during sexual contact infection with a carrier;
- Transmissible - through the bites of infected insects.
Also, the infection can penetrate into the body during medical procedures using non-sterile instruments.
note! The input gate for the penetration of infection with meningitis are nasopharynx, intestines and bronchi.
Many harmful microorganisms, which provoke the development of meningitis, always present in the human body. But in the presence of favorable factors they penetrate into the blood through the bloodstream and reach the cerebrospinal fluid and cause inflammation of the meninges.
factors, in which infectious agents are activated in the body, can be:
- Chronic malnutrition and chronic fatigue syndrome;
- Diabetes;
- peptic ulcer disease;
- Reduced immunity against a background of chronic diseases;
- AIDS virus;
- Metabolic disorders.
As meningitis can occur as a complication of pneumonia, sinusitis, suppurative otitis media, or as a consequence of traumatic brain injury.
Types of meningitis and symptoms
Infectious meningitis has several varieties and are classified on several grounds: by localization, stream, severity, the nature of the inflammatory process, etiology and origin. Depending on the type of disease may be different clinical picture of meningitis.

Consider the most common form of the disease:
- bacterial meningitis (caused by bacteria) - characterized by sudden onset and rapid increase of clinical symptoms. The incubation period is two to twelve days. After contact with pathogens in blood is accompanied by attacks of chills, the rapid rise in temperature, painful headaches, nausea, vomiting.
- Viral meningitis - symptoms usually grow for a few days. Onset of the disease is similar in features to the common cold, but over time the symptoms begin to grow. Blurred initial symptoms can lead to an incorrect diagnosis, that can cause dangerous and irreversible consequences.
- Purulent meningitis - most commonly caused by bacteria (meningococcus). The meninges accumulated pus, that provokes a rapid increase in symptoms, and is characterized by very severe disease. The first symptom of the disease - a sharp rise in temperature (to 40 degrees), the appearance of pain (headaches and muscle), the occurrence of seizures, vomiting, nausea, photophobia.
- Serous meningitis - compared with purulent differs less severe, when it occurs, there is an increase of lymphocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid. More common in children, than in adults. Pathogens can be, as bacteria, and viruses. Key features: rapid temperature rise (to 40 degrees), gastrointestinal disorders, pain in joints and muscles, intense headaches.
- Meningococcal meningitis - the most dangerous form of the disease, wherein the purulent contents accumulated in the meninges and edema, that the untimely helping lead to death.
- Tuberculous meningitis - occurs when penetration into brain membranes tubercle bacillus. It is the appearance of the first signs of weakness and lassitude, gradually causing severe muscle and headaches, accompanied by muscle stiffness in the neck and neck. Nausea and vomiting are not common with this sort of disease, but the frequent companion of tuberculous meningitis is the emergence of arrhythmia.
By the nature of the course and, depending on the rate of increase of meningitis can be lightning (develops within a few hours, during the day, death can occur), acute and subacute (symptoms increase for a period of three to fourteen days), chronic (symptoms may grow for 4 or more weeks, typical - for tuberculosis forms).
Besides, for meningitis may be complicated by the presence of other diseases, which also affects the development of disease symptoms.
The main symptoms of meningitis
Meningitis is quite symptomatic, but its symptoms are often mistaken for an ordinary catarrhal viral disease. As a result, symptoms are removed taking medications, making it difficult to timely diagnosis of the disease.
The incubation period can last up to seven days, during which symptoms can occur obscheinfektsionnye:
- The rapid rise in temperature (to 39-40 degrees);
- Lack of appetite, nausea;
- Fever or chills;
- Blanching of the skin;
- Muscle aches, joints, headaches.
These symptoms are usually not serious, so very often it comes to, disease that flows in a dangerous step, difficult to treat.
The main symptoms of disease are the so-called meningeal signs, when they appear, should immediately seek medical help.
The main signs of meningitis in adults:
- Headache - the main symptom of meningitis, having the identifying characteristics of: constant and intense, Pain increases when turning the head to the side and up and down, there is a feeling of "fullness" inside the skull, pain gets worse in bright light and loud sounds.
- Increasing the temperature to high rates. There is usually a high fever in the first days of the disease, at the same time bring down the indicators is difficult.
- Nausea and vomiting. One of the clearest symptoms of meningitis - vomiting "fountain", appearing on 2-3 day of illness. The occurrence of vomiting is not dependent on food intake, and no relief.
Other meningeal signs may not exhibit, depending on the type and nature of the disease. These include:
- hyperesthesia (skin sensitization) - even with a light touch of a person is experiencing pain.
- All that- and zvukochuvstvitelnost (fear of bright lights and loud noises).
- disturbances of consciousness: lethargy, distraction. The patient "retardation" is different - questions answers slowly, may not respond to the appeal of others.
- Cramps - may experience twitching of upper and lower limbs, with the rapid development of the disease are frequent spontaneous bowel movements and urination.
- Mental disorders. Because of violations of functions of the brain can occur hallucinations, unjustified aggression or apathy.
- visual impairment. If the inflammatory process backlog optic nerves, may have a squint, nistagmo (fluctuation of the eyeballs), diplopia (split predmetov), decreased vision.
If meningococcal infection characteristic of the disease is the occurrence of rashes as a dark red character dot hemorrhages.
Important! Older people have symptoms of meningitis are usually "lubricated": vomiting and headache may be absent, more common - drowsiness, tremor, various mental disorders.
Specific signs of meningitis, distinguishing it from other diseases, It is a muscle contracture. This term means, that in certain muscle groups of the increased amount of cerebrospinal fluid occurs painful tension (rigidnostь). How to check?
Muscle signs of meningitis:
- Tonus neck. One can not press your chin to your chest - when he takes a horizontal position, head itself deviates ago. In this case, the neck muscles seem hard to the touch.
- syndrome Kern. The leg of the patient to bend at the hip - a person is not able to independently align the knee, tk. rear thigh muscles will be in good shape.
- syndrome Brudzinskogo. The lower sign - by bending one of the lower limbs at the hip and knee, the second bend reflexively. The average feature - if the pressure on the lower abdomen, legs themselves bent at the hip and knees. The top sign - if you tilt the patient's head to his chest, feet as, as in the previous case,, bent reflexively.
Meningitis is diagnosed based on a combination of common, meningeal signs and muscle. But the exact diagnosis is possible only in a hospital after a series of clinical trials.
How to cure meningitis
Assigning regimens occurs only after, the patient was carefully examined, tk. for the proper course of treatment it is important to identify the type of meningitis, its degree of development, localization of disease and pathogen, which caused inflammation.
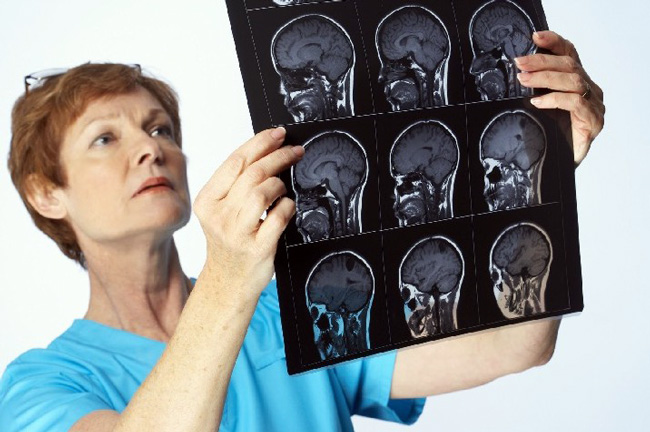
diagnosis of meningitis:
- Analysis of patient complaints.
- Inspection of neurological signs (muscle contracture).
- Laboratory examination of blood (to assess the basic indicators of the presence of inflammation).
- CT and MRI scans - used to diagnose meningitis complications, developing in the brain.
- Radiography - used, in the presence of foci of infection in the paranasal sinuses or lung.
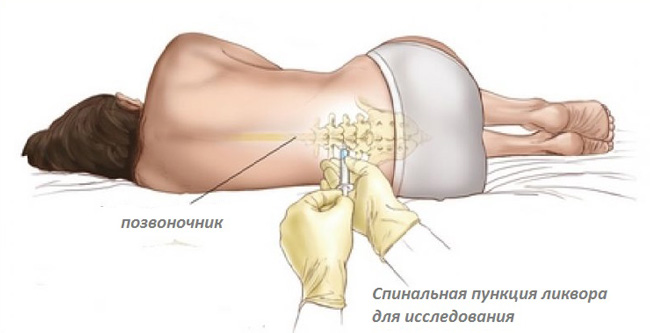
- Lumbar puncture - the main diagnostic procedure for the detection of meningitis. At the level of lumbar puncture is done with a special needle for tissue sampling CSF (cerebrospinal fluid). Assessment of the chemical and physical properties of the CSF allows to establish the etiology of meningitis: purulent meningitis liquor greenish-brown or whitish, with serous - Transparent.
Important! meningitis must be treated only in a hospital - the disease can develop rapidly and in a few hours can cause the patient's death. You can not self-medicate and use traditional methods for the treatment of meningitis.
treatment regimen:
- The destruction of the pathogen:
- When bacterial infections used antibiotics: penicillins (ampicillin, amoxicillin), tsefalosporinы (Tsefatoksym, ceftriaxone).
- Fungal lesions - antifungals (amphotericin, fluconazole).
- When viral meningitis - antivirals and immunomodulators.
- Reduced inflammation and swelling of the brain:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents (Tyempalgin, Acetylsalicylic acid, nimesil) reduce the intensity of headaches, fever, heat.
- diuretic (Uryegid, Diakarʙ) reduced pressure vnturicherepnoe, thereby reducing brain swelling.
- Dezointoksikatsionnaya therapy (droppers) - Actions infusion solutions introduced (crystalloid, colloids, sorbents and brines) to eliminate toxins, are products of vital activity of bacteria and viruses.
- Vitamin therapy - to maintain and replenish the body the necessary macro- and micronutrient.
Antibiotics are only used in meningitis, caused by a bacterial pathogen. They can be administered intramuscularly, intravenously, and in severe conditions - are introduced directly into the cerebrospinal fluid.
Time treatment started facilitates the patient's condition within the first 2-3 day, but some residual symptoms (recurrent headaches, intracranial pressure oscillations, et al.) can be felt even 2-3 months after the end of therapy, so patients should be at a constant dispensary.
Prognosis and complications
The viral form of meningitis have a favorable prognosis, with adequate and timely assignment of courses of therapy recovery occurs within 2-3 weeks. Purulent meningitis and bacterial species - the most dangerous, and a favorable outcome in this case is only possible when administered to the patient medication, inhibiting infectious agents, in the early stages of disease development.
Regardless of the severity of the disease and its variants in most cases, meningitis entails dangerous consequences for adults, tk. infection touches the meninges. Moreover, complications may develop during the disease and after his transfer.

During the development of acute meningitis, the patient may develop:
- Swelling of the brain - is accompanied by a disturbance of consciousness, sharp pressure jumps, tachycardia;
- Toxic shock - there is a strong food poisoning organism infectious agents of decay.
In these two cases,, if you do not provide emergency aid to the patient, coma and death - and the patient may die after only 2-3 hours after the active phase of the disease.
After suffering a mild form of meningitis in a while (6-12 months) there may be signs of postmeningialnye:
- Frequent and repetitive headaches;
- Reduced cognitive function and memory;
- gratuitous, spontaneous seizures.
With proper treatment and a favorable outcome of such symptoms usually disappear over time by themselves.
In severe forms of meningitis in humans at any time until the end of life may experience the effects of the disease, due to a general disorder of brain activity:
- epileptic seizures;
- Paralysis of individual body parts;
- Gidrocefaliâ;
- Restricting speech, thinking, motor functions;
- Deafness and loss of vision (full or partial);
- hormonal disruptions.
Meningitis - a disease, its dangerous consequences and high rates of mortality. Therefore, the symptoms of the disease should be aware of and comply with preventive measures to prevent meningitis infections - These include vaccination against viruses (rubella, meningococcus, mumps and TD), which allow to generate immunity against viruses, pathogens, as well as personal hygiene, timely treatment of chronic and infectious diseases, immunity strengthening.