The human body is alive and growing a huge variety of different bacteria and microorganisms: some of them are considered to be useful, others - pathogenic, harmful. Particular attention should be given to E. coli, inhabiting the intestines of each person - it is considered to be the source of many diseases, deadly for people with weakened immune systems, children and the elderly. In this article, the reader will learn important information about E. coli, symptoms of intestinal infection, its treatment, and other information.
Functions of E. coli in the human body
Coliform bacteria are necessary for human life. This group contains various microorganisms, called coliforms. They make up only one percent of the intestinal microflora and solve a number of important tasks:
- perform a protective function, preventing the development of disease;
- their presence contribute to proliferation of bifidobacteria- and lactobacilli;
- involved in the metabolism of fats and cholesterol;
- participate in the development of vitamin B (the entire group) and K;
- improve the absorption of compounds with iron and calcium;
- strengthen the system behalf of children (to 7 years old).
Exposure to E. coli useful invaluable throughout life, but pathogenic strains of these bacteria provoke disease, cause poisoning, destroying valuable intestinal environment, destructive effect on the immune system of adults and children. In the latter case it is doubly dangerous, fragile because the child's body becomes vulnerable to the corrosive environment.
Attention! E. coli is very dangerous during pregnancy: infection is able to penetrate into the fruit, develop the disease and lead to miscarriage.
E. coli are quite stable, they are able to survive for some time, even leave the human body. This helps in medical research and treatment, collecting information by means of stool analysis, urine, etc..
Danger of intestinal infections

Modern scholars dressed four classes of pathogens; there are over 100 types of pathogens, causing gastrointestinal disease (gastrointestinal tract). What consequences they threaten?
- Actively multiplying in the large intestine, microorganisms cause malfunction of its secretory function, increase the amount of fluid, dilution chair.
- hemolyzing strains (fall into one of subtypes of E. coli) produce verotoxins, that can become a cause of colitis and necrosis. Microorganisms damage vessels, interfere in blood supply. Moreover, once in the bloodstream, they infect the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. If the bacteria get into the abdominal cavity, they cause peritonitis.
- After contact with microorganisms from the external environment affect the reproductive system organs and can cause inflammation of the prostate, testicular, appendages of their men; oophoritis, vagina, cancer in women.
- Intestinal infection infects the kidneys, urinary tract.
- Related to this group of bacteria are the cause of meningitis in newborn infants.
this disease is also highlighted, as the hemolytic uremic syndrome. It occurs when a weak immune system: children and babies, older people, women after childbirth. Hemolytic E. coli forms verotoxins, which poison the body.
Under their influence blood platelets stick together, creating a disturbance in the blood movement. there are blood clots, which violate the kidneys, can lead to tissue necrosis. Erythrocytes also damaged: because of this there is jaundice (Skin becomes lemon shade).
This is a dangerous disease, that requires proper treatment. Half of the patients developed brain swelling. AT 30% situations develop kidney disease, capable of causing lethal (to 7% cases).
Attention! Describes only some of the possible consequences of intestinal infection.
There are other types of staphylococci and streptococci, causing disease throughout the body, up to a brain abscess and death.
Symptoms of intestinal infections

The causative agent of the disease may enter the human body in the following ways:
- cooking or eating food with dirty hands;
- the use of unwashed foods (vegetables, fruit);
- eating meat roasting weak;
- use of contaminated water.
In the latter case there is a risk, even when swimming in rivers, lakes and other natural waters. After that, a person must be sure to take a shower and wash away bacteria.
If the following symptoms are advised to contact the hospital (clinic) and pass tests on feces, urine, strokes:
- The most important feature - indigestion. When the development of an intestinal infection take the first blow gastrointestinal organs. If the urge to diarrhea (false or real) repeated until 10 once a day, or diarrhea occurs within a few days, an urgent need to go to the survey.
Attention! Pathogenic E. coli in infants is accompanied by a pronounced fermentation: abdominal pain, meteorism.
- Cal has a sharp odor uncharacteristic (sour, putrefactive), frequent diarrhea (diarrhea) They may be accompanied by a release of blood.
- The patient loses fluid, characterized by a constant thirst.
- Man loses appetite, breath becomes sharp, unpleasant. Frequent vomiting may occur.
- With the development of the disease the patient is flaccid and weak, It is sometimes accompanied by an increase in body temperature to 38-39 degrees.
Symptoms are clearly manifested at the end of the incubation period, takes less than 3 days from the day of infection.
Methods for detection of E. coli
When an intestinal infection crucial disease diagnosis method, which will help determine the specific type of bacteria, to find the right method of treatment and to take timely action.
- Method of bacteriological research, conducted with a variety of crop materials:
- if suffered intestine, analyzing the feces or vomit;
- in lesions of the urinary tract, analyze urine;
- in the case of infection of the genital organs, taken swab or scraping with mucous.
The materials are placed in a special environment, in which microorganisms multiply; Then they are tested for sensitivity to antibiotics. This helps the doctor to appoint the most effective drugs for treatment.
- Method of research using special medications involves the use of ultrasound, urography, etc..
- Method general widespread clinical studies. It does not allow to detect pathogenic bacteria, but can confirm the presence of inflammation in the feces, urine, pus or blood. It used as a supplementary method of diagnosing.
The genitourinary tract microorganisms occur during anal sex and non-observance of the elementary rules of hygiene. Bacteria enter the urinary tract from the gut, fixed in them and not washed out completely during urination.
Coliform bacteria during their presence in urine is not a sign of infection. This may be a manifestation of pathologic changes in the urinary system.
E. coli in a smear in women is a consequence of:
- wearing tight underwear;
- unprotected anal sex;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules.
During pregnancy, the presence of pathogenic bacteria is risky for the baby. E. coli in the vagina is able to go to the child during birth and cause meningitis.
Attention! The mother's immune system can not get into the fetus through the placenta and protect it. Before birth, women need to carry out an appropriate and accurate treatment.
How to treat E. coli: effective ways
If physicians have found E. coli in the analysis, you must determine the correct treatment. It involves not only the use of drugs, but the correction power, this contributes to improvement of the gastrointestinal tract and eliminate pathogenic bacteria.
Currently Gastroenterology identifies several directions for the treatment of intestinal infections:
- medication.
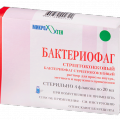
Here there are several groups of drugs: mainly, are antibiotics and probiotics, funds are also used for detoxification and bacteriophages (special viruses for destruction of harmful bacteria).
It is necessary to choose the right medicine: known, that E. coli rapidly increases its resistance to antibiotics. Sometimes true means really pick up only after the conduct of clinical trials, that will determine, to any substances susceptible microorganisms.
Duration of treatment the doctor determines. In some cases, required hospital treatment.
Council! Konchaniya after antibiotic treatment is recommended to take the drug for the recovery of the intestinal microflora.
- special diet.
It involves dietary restrictions. At the time of treatment is prohibited to use milk, milk products, pickles, raw vegetables and fruits.
If an infection is detected in the stool, used diet №4: eat only boiled or steamed food. cereals, pasta and milk products have prohibited. Sophisticated food - meat or fish - permitted only eat shredded, pasty form.
If pathogens observed in urine, used diet №7, which prohibits fat, sharp-salty food, mushrooms and sweet.
In the future, it is recommended to use yogurt to restore the intestinal environment, yoghurts and other milk products, that contain probiotics.
- Plenty of fluids.
To avoid dehydration is recommended to drink plenty of fluids: water (mineral or boiled), herbal teas (tutsan, oak bark, etc.).
In hospital treatment (in severe cases,) apply dropper. Depending on the individual features can be assigned to other medical facilities.

As a separate method may distinguish treatment folk remedies. Below is a recipe for a decoction made of artichoke, which will help in the treatment and subsequent recovery from infection.
Composition:
- 300 g. Jerusalem artichoke;
- 150 ml milk;
- 150 ml of water;
- 2 tablespoon butter;
- 1 tbsp flour (wholegrain).
- Finely chop the artichoke (cubes).
- Mix water and milk, boil, Boil the root to the soft state.
- Pour the liquid into a separate vessel, add the butter and flour. Stir until thick broth.
- Eat cooked artichoke and the resulting sauce.
This tool is great help in restoring the microflora, together with the above-mentioned products.
Treatment of intestinal infection - a long and unpleasant. The cause of this disease is largely hidden in plain irresponsibility. Avoid getting pathogens in your body just, you just follow the simple rules of hygiene: cooking, during sex, taking a shower.
With the help of this article appeared reader informed about the main features of E. coli, consequences of the disease and its treatment. This information will help to take the necessary action in the event of unusual situations.