Infektsionnыy mononucleosis or angina monotsitarnaya, also known under the name of the disease and benign limfoblastoz Filatov - an acute disease of viral origin, the symptoms resembling angina, and proceeding with primary involvement in the inflammatory process of the mucous oropharynx, lymph nodes, spleen and liver. The disease accompanied by a characteristic change in the blood of formula, by which it got its name. Infectious mononucleosis in adults and in children occurs with varying frequency - mononucleosis cases of the disease among young adults most often recorded 20-30 years old. The disease responds well to treatment.
What is mononucleosis?
Pathogens may include the following viral agents: Epstein-Barr virus (predominantly), and herpes virus 6 type and cytomegalovirus. In some cases, the cause of the disease becomes a combination of. Reservoir of infection and its source can be a man, as with pronounced manifestations of the disease, and suffering from mononucleosis were obliterated. Less commonly, infection is transmitted from clinically healthy carriers of the virus.
Ill patients begin to excrete the virus in the environment is still in the incubation period, from its second half. Isolation of infectious agent continues after occurrence of primary infection for another 6-18 months. Besides, the presence of the virus is also confirmed in 15-25% clinically healthy seropositive patients.
In its call hit as main pathways in an organism viral agent:
- in the mouth with a kiss with patient saliva or releasing the carrier virus, with microscopic drops of sputum and saliva from the patient coughing or sneezer;
- using common objects hygiene and cutlery;
- during blood transfusion, through the untreated reusable syringes;
- intercourse;
- from mother to child across the placenta.
note! The risk group with mononucleosis include family members of the sick, as well as his colleagues or members of any team, wherein the flare of the disease was recorded.

A person's susceptibility to the virus, causes acute and chronic mononucleosis high, but, much more likely to be recorded and erased lighter forms of the disease. The extension to contribute mainly immunodeficiency.
symptomatology
Today decided to allocate typical and atypical varieties of flow mononucleosis.
Besides, the disease is divided into acute and chronic mononucleosis.
note! A separate form of the disease is an infection with the Epstein-Barr patients, suffering from immunodeficiency disorders of various origins and those, Living with HIV.
- The incubation period for the development of mononucleosis vary widely - from five days to one and a half months since, as an infectious agent in some way has got into human organism. After that, it begins to replicate and spread through the circulatory system.
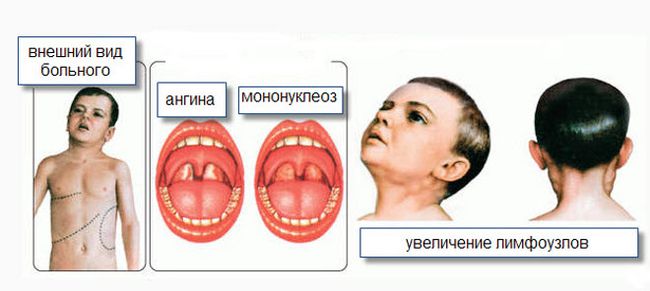
The virus also accumulates in the lymph nodes. That is why from the very beginning, patients have an increase in their. Most often in the process are involved occipital, zadnesheynye and submandibular lymph nodes. With the development of the disease, they are sealed, staying mobile and painless, in some cases, become a little tenderness.
- With the development of the disease possible period without forming any specific symptoms. With this film the main feature of the disease becomes a redness of the tonsils, as well as the oral and pharyngeal mucous, which is accompanied by raising the temperature to subfebrile, headaches, malaise, weakness, nausea and congestion of the nasal passages. of course, All these signs are not the basis for the diagnosis of "mononucleosis", even prior.
- Most often the disease develops acutely, namely as follows:: the patient has a fever, he feels severe nausea, body aches, loses appetite, He suffers from severe headaches. This condition can last from a matter of days or stretched for a two week period.
- Thereafter, the patient is formed by a triad of classical signs of specific diseases mononucleosis:
- increase in body temperature to 38 ° C and higher without increasing perspiration (this fever can last up to 1 of the month);
- swelling and slight pain in the lymph nodes;
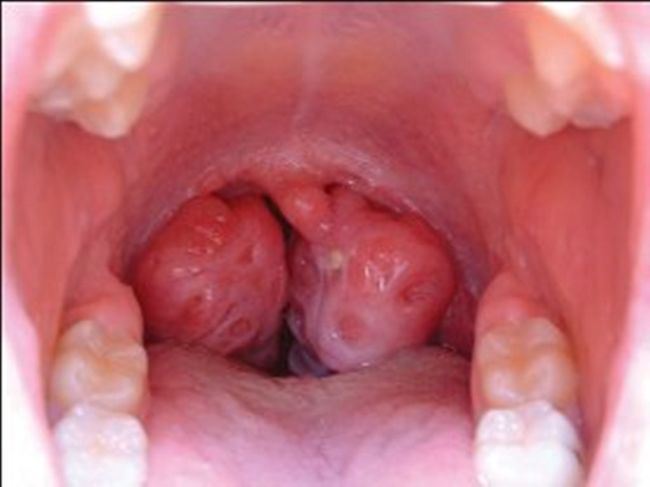
- sore throat (soreness, hyperplastic changes and follicular throat; redness, friability and tonsils edema, where there is a yellowish-gray powder, Easily removed by mechanical means - a cotton swab).
Often, patients have a characteristic skin rash (cm. pictured below) and on the mucosa of the soft palate:
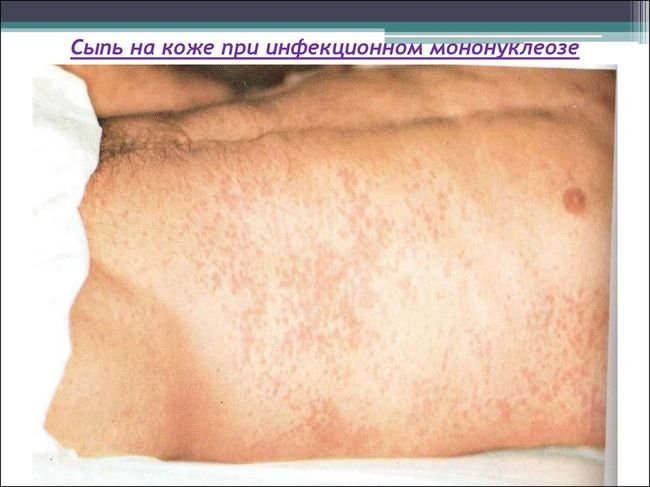
The liver and spleen of the patient sometimes increase in size, in some cases there is a yellowness of the skin. Sore throat is constantly growing until even the inability to swallow solid food and their own spittle, as it brings the patient suffering.
Progressing nasal congestion, vote, if the patient does not lose it at all, acquires a "nasal" sound.
- After about two or three weeks the symptoms of the disease begin to gradually weaken, comes to recovery.
- but, the disease can be quite long and reach up to six years, if it develops with periods of remissions and exacerbations (chronic mononucleosis).
- With the full consequences of convalescence acute form of the disease are absent, despite, that the agent can continue to persist in the blood. In this case, the disease does not return.
Complications of mononucleosis develop not so often. The most common of these is otitis, may develop paratonzillitov, sinusitis and pneumonia (more often - in children).
In very rare cases, patients developed hemolytic anemia. Besides, dangerous, but very rare complication of mononucleosis is rupture of the spleen, coming because of its dramatic increase.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture as a whole, as well as on the basis of the results of research with the identification of a patient's blood in her atypical mononuclear cells in combination with the elevated levels of lymphocytes and decreased white blood cell count.
It is also worth to assign the patient to test for antibodies to the virus, caller disease.
So, most important factor, confirming human infection with this disease, is the detection of blood in his laboratory by atypical mononuclear cells in an amount greater 10%.
What to do if you suspect a disease
In identifying at mononucleosis symptoms need to seek help from a therapist or district directly to infectious diseases doctor.
In course of the disease in the form of a mild and moderate, treatment of infectious mononucleosis in adults can be carried out at home. Desirable to be compliance with bed rest, but, the question of its necessity is decided depending on the severity of symptoms of intoxication.
During the period, of not less than six months after recovery, the patient continues to conduct medical check-up, which involved local therapist, infectious diseases, and other specialists (depending on the severity of the disease). Convalescent patients during this time is not recommended physical activity and psycho-emotional stress.
mononucleosis treatment
Mononucleosis Treatment in Adults, especially if it is done at home, It involves the use of disposable or personal cutlery and crockery, and the exclusion of close contact with family members and friends.
Treat mononucleosis must be combined. The choice of drugs is due to the degree of severity of various symptoms.
- All patients will show antiviral agents, such, how Groprinozin, Valytreks and Acyclovir, Valtrex.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used as antipyretic and cropped in pathological inflammation foci. For this purpose, suitable Paracetamol, ibuprofen, nimesulide (Friends).
note! Taking in this disease not only acetylsalicylic acid is not shown, and it is strictly prohibited!
- To remove the swelling tonsils, oropharynx and spleen prescribe drugs from the class of antihistamine: Tsiterizin, Loratadin, suprastin.
- Sometimes patients shows an application specific immunoglobulin against Epstein-Barr virus.
- If necessary, (with a view to the relief or prevention of complications) in some cases, patients prescribed drugs from the group of glucocorticoids (prednisolone), and antibiotics (except for a number of drugs ampicillin).
- If the patient suffers from dryness and soreness in the throat, it is recommended that local treatment - treatment of the mucosa using Chlorhexidine, Furacillina or Gevaleksa.
Diet for mononucleosis plays a significant role in its treatment. Patients assigned table number 5, eliminating the use of animal fats, and smoked, acute, fried and pickled foods. Besides, it is recommended to give up sweets, alcohol and coffee.
Very useful are the chicken broth, yogurt and kefir, desirable natural, to leaven the basis. Besides, patients will be useful non-acidic juices or compotes.

To speed up the recovery of patients, as well as to facilitate the symptoms of the disease, along with a drug therapy treatment is indicated by folk remedies.
for example:
- using tincture of Echinacea can boost immunity;
- the use of a decoction of calamus or ginger prevents layering of secondary bacterial infection and helps to reduce pain in the throat;
- and elderberry and dandelion quickly soothe headaches and significantly strengthen the weakened body disease.
- And most importantly, that there is a surprising medicinal plant in nature, having a pronounced antiviral properties, which can be used as etiotropic therapy!
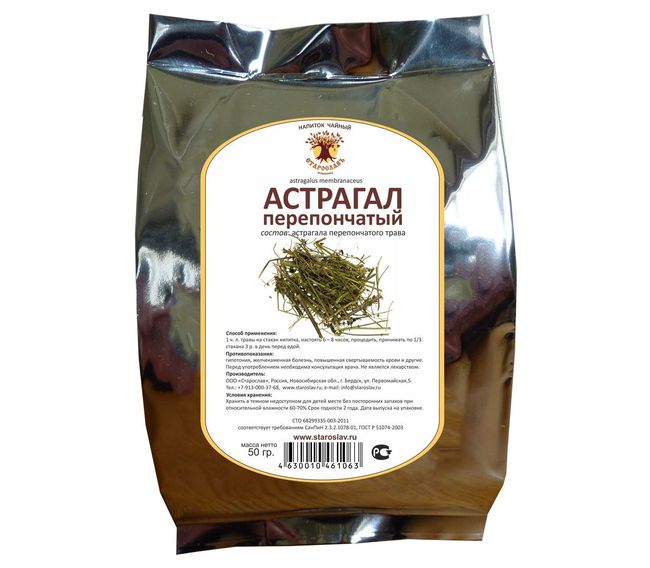 it Astragalus, and from preparing:
it Astragalus, and from preparing:
- Infusion: crushed root in a quantity of 1 Pour a tablespoon 200 ml just the boiled water and keep in a thermos 1-2 o'clock, then cooled, filter and take ½ cup 3-4 times a day.
- Broth: crushed root in a quantity of 6 g. pour 200 ml of water, heated on a steam bath for 15 minutes, and then insist 1-2 hours in a warm place. Take the same scheme, as an infusion.
During the period of recovery and long after patients need rest, proper nutrition, sleep and vitamin therapy (Supradin, VITRUM, Komplivit).
prevention
specific prevention, Alas, It has not yet been developed. A general preventive measures are exactly the same, as in other respiratory diseases. The causative agent of mononucleosis is not considered vysokokontageoznym, so no need for disinfection of objects, were in use in a patient or carrier. It is important to take measures, aimed at the general strengthening of the body and increase immunity.
Prevention of infection is the most basic hygiene rules, using individual cutlery and toothbrushes, careful monitoring of blood donations for the presence of viruses in it.