What is leprosy
leprosy (leprosy, Hansen's disease) - about it at least once in my life I heard everyone. But what kind of disease? The etiology of this disease is caused by the penetration into the human organism Mycobacterium leprae. This chronic infection is characterized by lesions of superficial tissues and peripheral nerves. The disease is manifested in two basic forms and two intermediate:
- Tuberkuloydnaya
- lepromatous
- Lepromatoznaя-border or border-tuberkuloidnaя.
note! In a number of cases detected early infinitive form. It can either develop into a full-fledged disease, and end with spontaneous remission.
How it develops
Leprosy is equally contagious for people of all ages, although cases of registration of the disease in children under one year of age are extremely rare. The peak incidence in children accounts for school age up to ten-year (order 20% of all cases). In children, the disease affects both boys and girls with equal frequency, but adult disease occurs twice as often in men, than women.
The causes of most cases of leprosy are in direct contact with the patient and transmission of infection from him. In the animal world are carriers of infection armadillos, and, most likely, lower primates, but they play a special role in the spread of the disease in the human population.
So how one can become a source of infection, long before the appearance of the first signs of it, the risk of transmission increases 8-10 time among members of one family.
The exact localization of the causative agent of implementation has not been established conclusively, but, probably, infection occurs through mucous upper respiratory tract and the skin. The main exit gates of infection is considered to be the mucous membrane of the nasal passages nelechaschihsya patients, lepromatous form of leprosy sufferers.
You can also send the pathogen through breast milk from a sick mother or the bites of blood-sucking arthropods, but in terms of epidemiological importance of these factors, very few.
The incubation period of this disease is quite durable - he is away from 3 to 5 years at a typical flow of infection, and ranges from 6 months to decades when other cases of infection.
Symptoms of the disease
The first signs of the disease is most often found on the skin in the form of one or more hypo-- or hyperpigmented areas (stain and / or plaque). At such sites, marked sensory loss or paresthesia.
If you examine the people, stationed in contact with the patient, especially for children, then they often find a single focus on the skin, often eliminated spontaneously during 2-3 years old. However, these patients also showed treatment.
Tuberkuloidnaya leprosy
- The early period of tuberculoid type of leprosy is most often takes place with the only symptom - clearly demarcated hypopigmented skin areas with reduced susceptibility.
- Then, these lesions grow, their edges are raised above the skin surface and rounded, sometimes getting the form of rings. There is a tendency for them to spread from the center to the periphery, while in the center there are the healing process.
- Fully formed lesions completely lose sensitivity, affects the sweat glands and hair follicles. Foci are few and asymmetric.
- Nervous tissue is involved as early in the disease process, superficial nerves, which are located in the hearth area, increase in size so, that become visible. Especially noticeable change in peroneal, elbow and large ear nerves.
- Pain along the nerves gradually increase and become unbearable character.
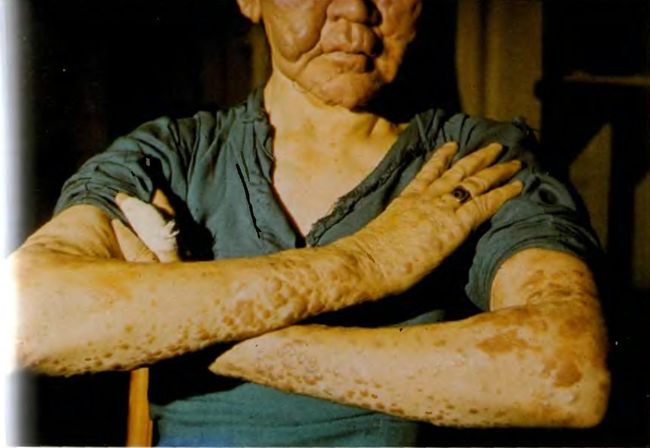
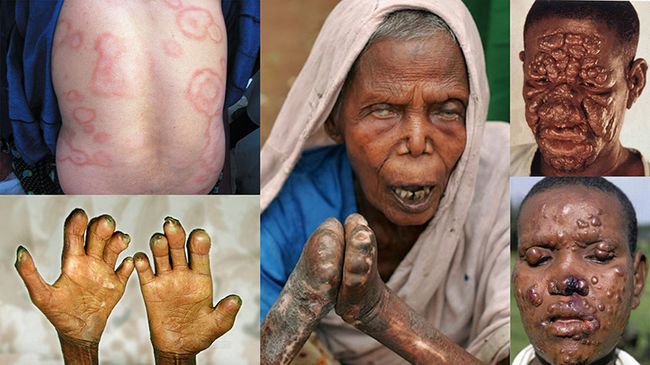
- As a result of nerve damage develops atrophy of muscular system, the most susceptible to changes in the muscles of the hands and feet, generating a characteristic contractures especially the small muscles of the hand. Often develop contractures of the hands and feet. Additional trauma leads to secondary infection with the hands and feet and to the formation of plantar ulcers. Later may be formed resorption and loss of the phalanges (as in the photo below)
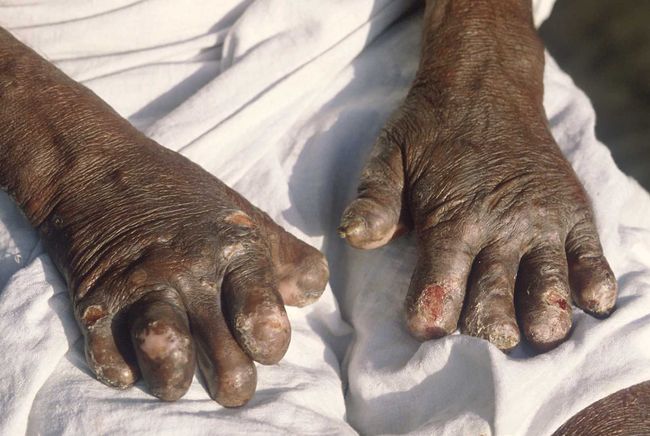
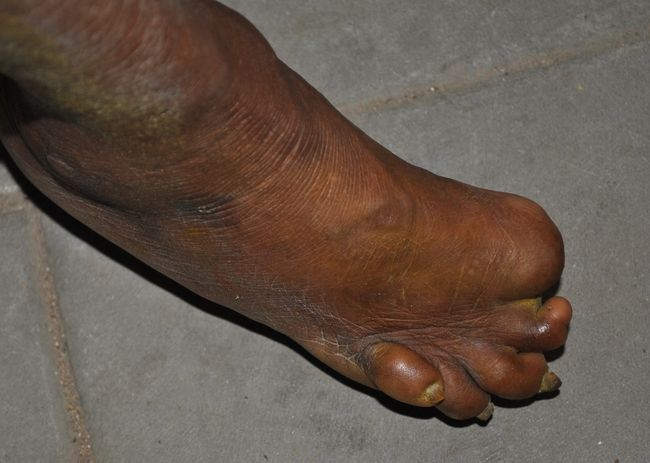
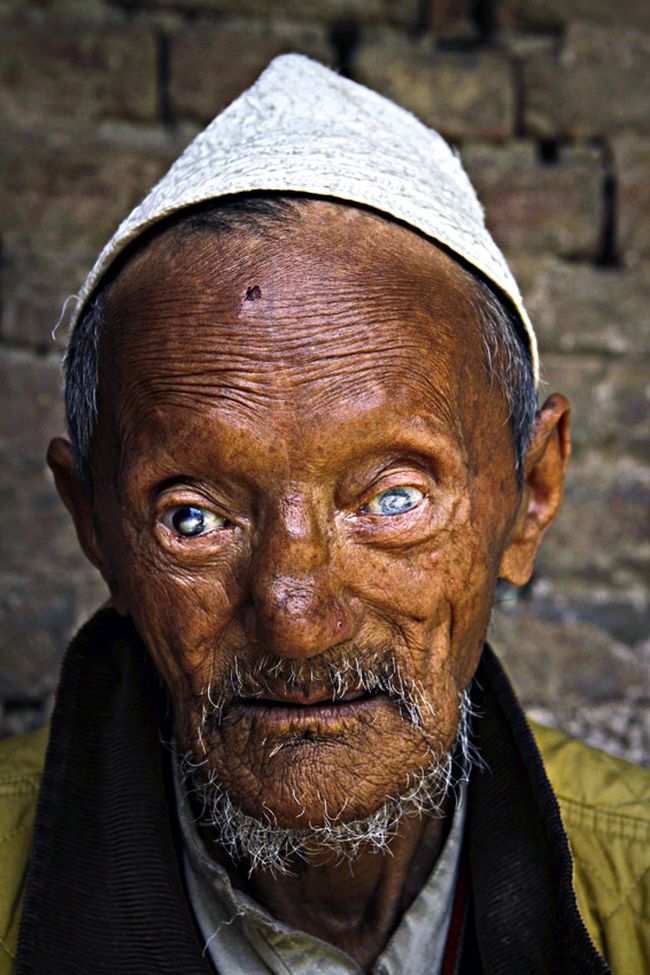
- If the process involves nerves facial, it is accompanied by the formation lagophthalmos and ulcerative keratitis, leading eventually to blindness (cm. a photo):

Lepromatoznaya leprosy
- Lesions appear on the skin in the form of nodules, spots, plaques and papules. Pigmentation in place these structures is weakened, they have clearly defined boundaries. Their central part, Unlike formations at tuberculoid form of the disease, convex and sealed. On areas of the skin, arranged between these foci, observed diffuse infiltrative changes. Most often, the centers are located on the face, in elbow, wrists, knees and buttocks, but can also occur in other parts of the body.
- As the disease in the pathological process involved all the new areas of the body, gradually developing their infiltration, in some cases formed nodules.
- The patient fall hair in the eyebrows, especially with the lateral sides.
- Gradually, the skin of the face and thickens ogrubevaet, forming the so-called "lion face", droop earlobes.
- By common early signs also include:
- nasal congestion;
- bleeding from the nose;
- difficulty breathing;
- hoarseness, laryngitis;
- obstruction of the nasal passages;
- «Sedlovidnыy nose»;
- iridocyclitis, keratitы;
- gynecomastia, infiltrative changes in testicular tissue, followed by replacement with scar tissue, sterility;
- swollen lymph nodes in the groin area and underarms, painless palpation.
- Information about the involvement of the major nerve trunks in the pathological process in this form of the disease is not enough, but, with the progression of the disease is widespread, diffuse hypoesthesia in the peripheral extremities field.
Border form of leprosy
- Pathological lesions at the border and tuberculoid forms of leprosy in the skin are more reminiscent of pockets, forming at tuberculoid form of the disease.
- In this case, there are more, and the boundaries of their fuzzy.
- For this form of current leprosy, Unlike actual tuberculoid, characterized by the involvement of multiple peripheral nerve trunks in the pathological process.
- Besides, increased variability of various skin foci, This property has given rise to the second name of this form - "dimorphic" leprosy. Characteristic papules and plaques on the skin side by side with the centers of the spots.
- loss of sensation occurs, but it is less pronounced, than with purely tuberculoid during process.
- Border lepromatous form is manifested in patients with skin heterogeneous foci, mostly symmetrical. ear lobe may be thickening, however, eyebrows and nose shape if change, insignificantly.
Treatment
There are modern and fairly effective drugs, to effectively treat patients, According disease sufferers.
Council! When you start to leprosy, in order to avoid the formation of complications from respiratory, musculoskeletal and nervous systems, as well as the visual organs advised to undergo further consultation following specialists:
- neurologist;
- otolaryngologist;
- orthopedist;
- ophthalmologist;
- physiotherapist.
- The mainstay of treatment of this disease is a 4,4-diaminodiphenylsulfone (DDS, Dapsone), folate antagonist
The dose varies from its 50 to 100 mg in adults. This formulation is cheap, shows even pregnant, comfortable (apply 1 once a day).
note! Despite, that a few days of application of the drug kills almost all mycobacteria, non-viable micro-organisms can be detected in the samples, of patient, for five - ten years. Besides, even a few surviving bacteria are able to wait for long-term periods, to cause a relapse.
- Rifampicin - fast-acting antimicrobial, leprosy destroys the pathogen to undetectable levels for five days after a single oral dose 1500 mg.
However, cost-effective use of the drug in the amount of 600- 900 mg once monthly not supported by sufficient amount of Research and still unnecessarily. therefore, to obtain more reliable data, Rifampicin is recommended to assign daily or twice a week, on the old proven scheme.
Resistance schtammov leprosy to this drug is almost not found.
- Klofazimin (Clofazimine) - a drug, active substance derivative is phenazine dye.
Dosage ranges from 50 to 200 mg / day. It has toxic effects on the skin and gastrointestinal mucosa. Currently, the study is still ongoing use of the drug in the disease leprosy, although it is already being used in practice.
When a specific event is known, that this strain of leprosy mycobacteria sensitive to "dapsone" drug, in the treatment of limited combination of two drugs - rifampicin and dapsone. but, available at the probability of resistance to pathogen dapsone (secondary stability) justified the appointment of a third drug will. The same will be true with the lepromatous form of leprosy flow.
In the course of the treatment of the patient are taken to study biopsies and scrapings from the skin - as long, until the result will be negative staunchly. Usually the treatment takes at least two years. If the patient is suffering from lepromatous form, the duration of treatment is not limited to any terms, it may remain for life.
for example, in the United States in the presence of disease in a patient with a small bacterial load and lack of lepromatous form - appointed twelve-course "dapsone rifampicin +", and then the next twelve-month rate of dapsone.
On the second or third month of drug therapy should be noticeable objective visual signs of improvement in the patient's condition. Neurologic manifestations also have a lesser degree disturb convalescent.
Reactive states leprosy
- Erythema nodosum is a mild form lends itself well to therapy, antipyretic and analgesic agents.
- erythema, be severe, treated with higher doses of drugs:
- prednisone (appointed in dosage 60-120 mg / day). Antibakterivalnaya therapy during its continued application of, as the group of corticosteroids drugs increase survival leprosy pathogen in humans in the event, if no drugs are used antileprosy.
- Rifampicin increases prednisone metabolism in the liver, making reasonable increase in its dosage to achieve a positive treatment effect.
- thalidomide (Thalidomide) - the most effective drug for the treatment of leprosy-associated erythema nodosum. It is administered at an initial dose of 200 mg 2 times / day. patients, chronic forms of the disease the dosage is gradually reduced to lower maintenance dose, namely 50-100 mg / day.
note! Thalidomide is absolutely contraindicated in women of childbearing age because of its teratogenicity, However, the rest of the contingent of leprosy patients it does not cause significant side reactions.
- Clofazimine - antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drug, found application including the treatment of chronic leprosy-associated erythema nodosum. However, just, to his body a sufficient level has been reached, you need to take it for three or four weeks, so the acute forms of the process, requiring urgent treatment, its use is not always justified.
- Other preparations of anti-inflammatory class are used in severe cases. Among them, the antimalarial chloroquine and a number of medium-cytostatics.
- When relapses, often occurs acutely, It is not uncommon irreversible damage to nervous tissue. In such cases, it decided to appoint:
- kortikosteroidы;
- klofazimin. Its use is indicated in a number of chronic disease. During the period of its application must be an extension of corticosteroid therapy.
note! The reaction of a number of recurrent defy treatment with thalidomide.
- Other measures. the majority of defects, leading patients to disability, can be avoided:
- widespread foot ulcers can be prevented, using shoes with soles compacted or special temporary dentures;
- carpal contractures prevented with the involvement of physical therapy in the treatment or use overlay plaster cast. In some cases, surgery is performed in order to reconstruct the destroyed tissue sites, including the transplantation of nerves.
- Held plastic tissue to recover deformations in the facial area, that helps to restore the patient's position in society.
- Severe psychological trauma, coupled with the isolation of the patient for a long time and with the change in his appearance, now reduced to a minimum by introducing the practice of home care and assistance of psychologists.
prevention
The fight against leprosy. Date basis for the fight against leprosy make timely case detection and preventive therapy form the basis of the fight against leprosy. The most important is the early detection of leprosy patients. In countries, endemic leprosy, necessary to carry out the annual population survey. In identifying such cases you need to check with leprominovoy breakdown of each member of his family and persons, contact with patients. the risk of transmission, even in untreated patients is relatively small, at their first admission to the hospital is not necessary to carry out any special measures to prevent the spread of the infectious agent. Chemoprevention dapsone in low doses effective and clinically confirmed, but, in most cases annually is sufficient to conduct a survey of contact persons.
Important! Vaccination antileprosy vaccine is currently being tested and is now recognized as quite promising.
If there are babies in the family of the ailing mother, they must be isolated from the patient and transferred to artificial feeding.
The other children without signs of the disease continue to attend school classes, but, they are examined twice a year.
In a laboratory detection of the pathogen in the body - they are assigned appropriate therapy, and they are temporarily transferred to home schooling or are hospitalized as.
note! In the locality, in which it is recorded frequent outbreaks of disease, Provide mandatory immunization of residents using the BCG vaccine. In the future it is planned to replacement antileprosy vaccine.
Patients, ever had a history of diagnosis "leprosy", are not allowed to move to other countries and may not hold positions in the food industry and child care. relatives of the patient with laboratory-confirmed leprosy in the active form are given specific preventive therapy. In order not to be infected with leprosy, you need to follow strict hygiene rules - just to handle microtrauma disinfectants and wash hands thoroughly with soap and water. If you have any suspicious skin formation - always consult a dermatologist to the district clinic.
If you have a suspicion of contact with an infected person with leprosy, should consult a doctor, infectious diseases, or directly to leprologist.