Today everything is less common in women, gonorrhea, symptoms and treatment are determined by qualified gynecologists and Venereology. Statistics show, that the incidence of gonorrhea has decreased to almost 2% cases of appeals. Given the fact, it can cause female infertility, such statistics can not but rejoice. However, must be considered, that the symptoms of gonorrhea in women often lubricated, but because of its diagnosis can be carried out already in the running phases of the disease.
Gonorrhea in women - it?
gonorrhea (tripper) - venereal disease, caused by the gonococcus Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Pathology is most often transmitted sexually. Not excluded the vertical route of transmission. Infection during pregnancy can lead to its premature termination and cause fetal hypoxia.
Gonococci can multiply not only in reproductive organs. His identify joint, light, eyes and other organs. A particular danger is complicated by gonorrhea, accompanied by a further secondary infection - Chlamydia, candidosis, syphilis. When running throughout the disease process increases the likelihood of blockage of the fallopian tubes and, as a result, infertility.
Ways of infection
The most common route of transmission - sexual contact. Getting on the mucosa, causative agent is embedded in it and begins to multiply. That is why the percentage of women is much higher incidence, than men. This is because, that during unprotected sex mucosa is contacted with a natural lubricant, whereas the natural urethra in the vagina can enter the secret is not immediately.
When unprotected sexual contact with an infected male likelihood of infection is about 50%. Such chances of contamination are equally relevant for both vaginal, and for anal intercourse. Oral sex, rate of infection below. But keep in mind, that gonococcal pharyngitis has no specific symptoms, and therefore the likelihood of infection is high enough in contact.
There is also a vertical path of transmission of gonorrhea. It is implemented by passing the baby through the birth mother's way. Gonokokki hit the surface of the skin and mucous membranes. As a result, the child may develop gonococcal conjunctivitis. Getting on the mucous membrane of the genital organs of girls, gonococcus causes gonorrhea newborns.
The probability of infection household by negligible. This is because, that the agent is unable to live a long time in the environment. There Neisseria quickly dies, thus losing the ability to infection. When using a common user items may come into contact to the mucous membrane of the pathogen, but, usually, its amount is not sufficient for the excitation infection.
symptomatology
A distinctive feature, How does gonorrhea in women, is blurring symptoms. This causes a lack of timely diagnosis and the impossibility of carrying out the treatment in the early stages of the disease. When men first pain during urination, evidence of infection, begin to appear at the end of the incubation period, the development of women in the body of gonorrhea passes without the expressed specific symptoms. therefore, usually, gonokokk detected on prophylactic examinations. almost 50% infected women gonorrhea does not manifest itself, and so diagnostics can be conducted in the period, when it began irreversible changes in the body. The first signs of gonorrhea in women can often be confused with symptoms of cystitis or thrush.
The main features of gonorrhea in women include the following:
- pain during urination, burning;
- severe itching in the genital area;
- frequent urination in small portions;
- yellowish discharge;
- in rare cases, fever.
Important! It should be remembered, gonococcus that can take root in the oral cavity, causing gonococcal stomatitis. For it will be characterized by the appearance of sores in the mouth, small erosions. they are located mainly under the tongue or on his back. Less common on the inside of the cheeks. Erosion covered by purulent discharge. Perhaps inflammation submandibular lymph.
Gonococci can multiply within the vestibule, hitting more iron. In this case, there is its inflammation, It called Bartolini. As a result, it increases to the size of a small plum and an education quite painful. Febrifacient, feel worse. Treatment of Bartholin carried out exclusively by surgery.
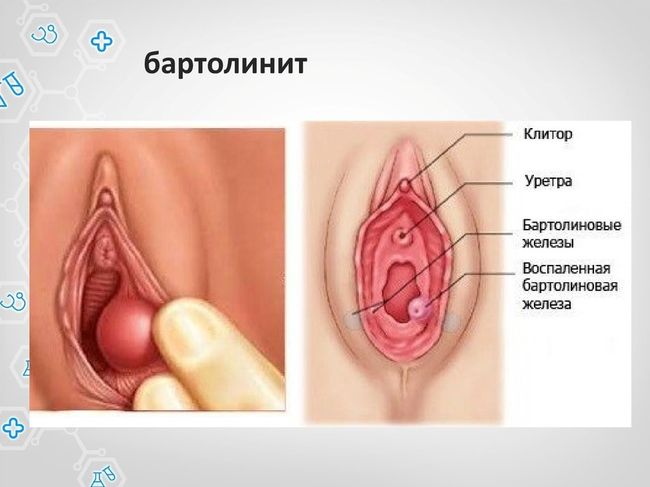
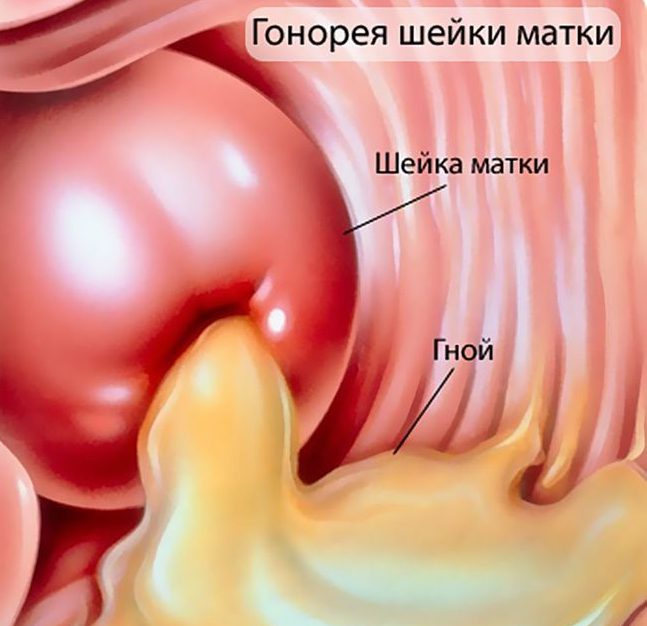
If Neisseria penetrates into the uterine cavity, This is manifested by painful sensations in the lower abdomen. menstruation dates slipping, intermenstrual bleeding may occur or isolation. uterine size increases, it softens and becomes painful. Symptoms of gonorrhea in women in this case may appear as a yellow discharge, and bloody, or streaked with blood.
The most seriously manifested gonorrhea in lesions of the uterus. He is accompanied by a sharp pain in the lower abdomen and raising the temperature to 40 0WITH. When such bonding occurs lesion lumen fallopian tubes, which leads to a violation of the outflow of purulent. As a result of the pipe is increased in size, it may, connecting to surrounding tissues. Gradually, this leads to the formation of tumor formation. If untreated, such damage can be completed peritonitis.
Gonorrhea and pregnancy
Gonorrhea in pregnant women detected during the mandatory inspection. Assuming, in which period there was an infection, gonococcus may have different effects on the fetus. It does not have the ability to pass through the placental barrier, and therefore can not directly affect the development of the baby.

The degree of influence on the course of pregnancy depends directly on, in which period began breeding gonococcal. Gonorrhea is the cause of pregnancy failures, miscarriage and abortion. Therefore, in the event of pregnancy in infected women is high probability of its interruption in the early stages.
Infection during pregnancy causes, gonokokk that can disrupt transport of nutrients between the placenta and uterus. As a result, the fetus may develop hypoxia, which may well be the reason for the delay of the baby. Also during infection Neisseria possible inflammation of membranes bubble envelopes. Infection of the child only at birth can occur from an infected mother. If the delivery was carried out by caesarean section, baby is not in contact with the gonococcus and, respectively, I was able to avoid infection. In the postpartum period in women can spread gonorrhea occur in the uterus.
methods of diagnosis
The diagnosis is carried out based on the execution complete examination. Usually, a gynecological examination for accurate diagnosis insufficiently. Additionally held swab for gonorrhea in women. For smear can be used as a vaginal discharge, and scraping from the cervix.

Gynecological examination revealed inflammation of the cervix and the characteristic signs of erosion. There may be drainage of pus from the cervical canal. There may also be its softening and tenderness.
In addition to writing a complete clinical picture used such methods of laboratory research:
- Microscopic examination of vaginal smears, urethra. Additionally performed by Gram staining. The effectiveness of this method is about 90% and this technique is currently one of the most common.
- Isolation of bacterial culture. It requires more time for diagnosis. It is used in the case of chronic illness and progress to identify comorbidities.
- PCR study. It is the most accurate, subject to all the necessary requirements in the conduct of. It should be noted, that this technique requires specialized equipment and complete sterility of the material under study. Therefore, it is used exclusively in the specialized agencies.
possible complications
In the propagation of gonococcal organism may develop complications such:
- Bartholin gland abscess;
- endometritis;
- salpingo-oophoritis;
- piosalpinks;
- piovar;
- formation and tubo-ovarian tumor development.
therapies
Treatment of gonorrhea in women is carried out exclusively based on the obtained clinical history. Usually, in the course of treatment using antibiotics, which inhibit the growth of gonococci. In pregnancy, treatment is carried out on the basis of hospital.
The regimen includes the use of different groups of drugs. Of the antibiotics most commonly used drugs penicillin group (Flemoksyn, Augmentin). Higher efficacy against Neisseria show cephalosporins (ceftriaxone, cephalexin). If there are complicated by pathology, which is also accompanied by chlamydia, Erythromycin is used or Rovamycinum. When pregnancy is strictly forbidden the use of fluoroquinolone antibiotics (ofloxacin), tetracycline (tetracycline) and sulfonamides (Biseptol).
Together with antibiotics applied immunomodulators, probiotics and gepatoprotektory. In pregnancy, further means are assigned to maintain placenta (Aktovegin, Trental). At the end of the treatment of gonorrhea in women is done through follow-up examination 7-10 days. Control tests are carried out during 3 months. Together with a woman, treatment is carried out and to her sexual partner. It is mandatory examination of children.
prevention
Prevention of gonorrhea in women is identical to the prevention of sexually transmitted infections. Woman as during pregnancy, and outside it, to abstain from casual sex. In the presence of ailments should immediately contact a doctor.